
Let it roooooolllll…..
March 2025
Sometimes we need a break and what could be more fun than an evening bowling?
Targeted PI3Kγ Inhibition Restores Liver Function in Sepsis Without Compromising Immunity
A groundbreaking study reveals a novel approach to treating sepsis-induced liver failure using nanocarrier-targeted delivery of a PI3Kγ inhibitor. Researchers engineered DY-635-functionalized liposomes to deliver AS605240 to hepatocytes via organic anion transporters selectively. This targeted strategy restored biliary canalicular architecture and excretory liver function while preserving immune defenses. The approach improved survival rates by 40% compared to untreated controls and avoided off-target effects on immune cells. By focusing on hepatocytes, the method mitigates cholestasis and inflammation without compromising immune responses, marking a significant advancement in sepsis care. This innovation opens new possibilities for precision nanomedicines in treating systemic inflammatory diseases and organ-specific dysfunction in critical illnesses.
Jen’as Long Night of Science 2024
This year our team wasvisting the Center for Applied Sciences of the Friedrich Schiller University. We were moving out from our universty hospital to bring translation to the world of basic sciences. With our collegues from the www.ATHANA.net and industry partners, we projected translation from nanoformulation to medical use cases.

Mini Retreat 2024
It was soooo hot those days! We found some inspiration and ideas those days for the new year. Let’s take it on!
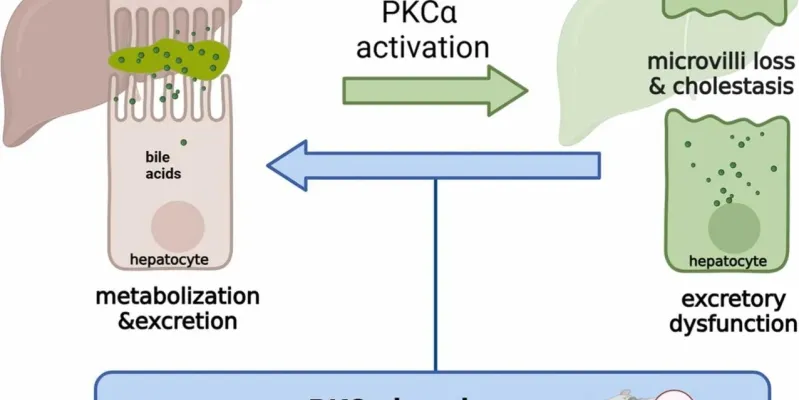
C alpha – a new drugable target in sepsis?
We’re thrilled to celebrate the outstanding work of Ling, the first author of a recent study that sheds new light on managing sepsis. Sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from a poorly regulated infection response, often involves liver dysfunction, which can significantly weaken the immune system. This research identifies protein kinase C-α (PKCα) as a crucial target for improving liver function during sepsis. By using PKCα inhibitors like midostaurin, the study demonstrates a significant boost in survival rates without compromising the immune response. This breakthrough opens promising avenues for novel therapies in sepsis treatment. Congratulations, Ling, on this impactful contribution to medical science!

Congratulations Ling! The Ph.D. is yours!
October 2024
Congratulations Ling for your graduation. Now it is Ph.D.!
Have a safe journey home and much success for your next endevours.
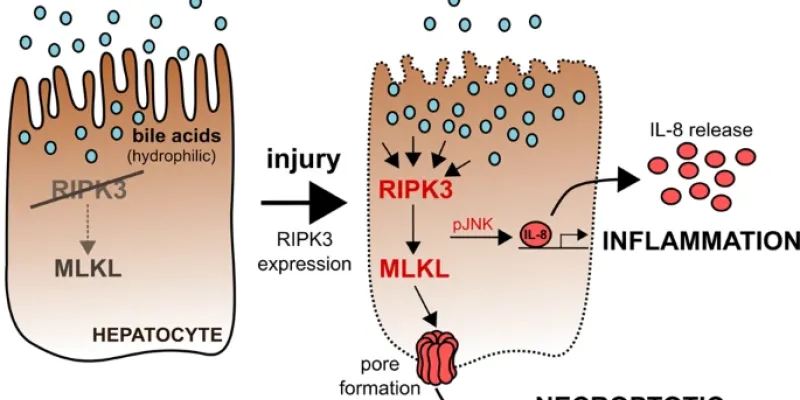
Congratulations Jessica for publishing!
April 2024
Jessica’s most recent study published in Cell Death & Disease reveals a crucial mechanism by which hepatocytes protect themselves from bile acid-induced inflammation and necroptosis. Researchers found that DNA methylation suppresses the expression of RIPK3, a key protein involved in necroptosis, in human hepatocytes. This protective mechanism is vital in preventing cell death and inflammation in liver diseases associated with cholestasis. The study highlights the potential of RIPK3 regulation as a therapeutic target for managing chronic liver conditions.